The U.S. Patent and Trademark Office’s precedential opinions on discretionary denial are the subject of significant attention—a withdrawn attempt by the Trump Administration to codify discretionary denial as a rule, a request for comments on rulemaking by the Office, and a challenge to the practice of discretionary denial as illegal under the Administrative Procedure Act.
The attention is deserved. Fundamentally, discretionary denial has harmed the patent ecosystem, reversing the positive changes observed in patent litigation frequency and cost. The changes even appear to have increased the cost of IPRIntellectual Property Rights. Usually associated with formal legal rights such as patent, trademark, and copyright. Intellectual property is a broader term that encompasses knowledge, information, and data considered proprietary whether or not it is formally protected. itself. Using cost data from AIPLA’s Report of the Economic Survey, decision analysis from Unified Patents, and statistical data from the PTOPatent and Trademark Office, informally used interchangeably with USPTO. itself, the following charts show a clear correlation of the implementation of discretionary denial and these negative impacts on the patent system.
PTO’s Discretionary Denial Changes
The primary drivers of the discretionary denial changes are the General Plastic (Oct. 2017), Valve I (May 2019) and Valve II (Aug. 2019), NHK Spring (May 2019), and Fintiv (May 2020) precedential decisions.
General Plastic created a set of non-statutory factors to be applied to determine if a prior petition by the same party justified denial of institution. Valve I and Valve II expanded this inquiry to prior petitions by other parties. NHK Spring included a brief suggestion that a parallel district court litigation may justify denial of institution. Finally, Fintiv expanded on that suggestion, creating another set of non-statutory factors used to deny institution based on proceedings in other forums.
Decrease in Institution Driven by Discretionary Denials
Over the past few years, the percentage of all denials that are based on procedural denials has steadily increased. Charts from Unified Patents illustrate this increase.
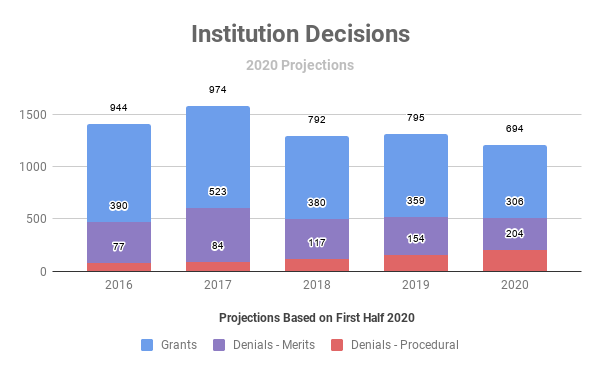
And, of these procedural denials, the vast majority are now derived from the § 314(a) discretionary denial decisions like General Plastic, NHK Spring, and Fintiv.
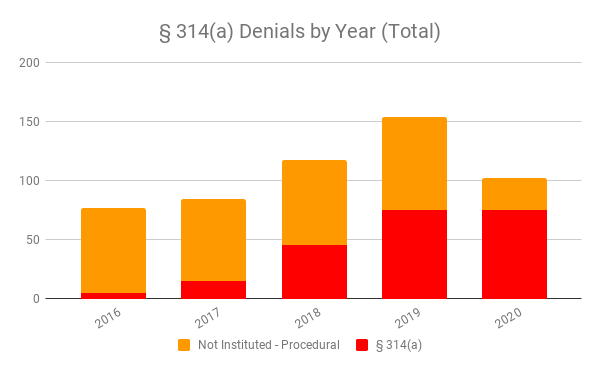
Discretionary denials were roughly constant prior to 2017; after General Plastic, they began to increase, and after Valve, NHK Spring, and Fintiv their usage accelerated rapidly, both in absolute number and as a percentage of all denials. And as procedural denials increased, the positive benefits of IPRIntellectual Property Rights. Usually associated with formal legal rights such as patent, trademark, and copyright. Intellectual property is a broader term that encompasses knowledge, information, and data considered proprietary whether or not it is formally protected. began to disappear.
Impacts of Discretionary Denial on Patent System
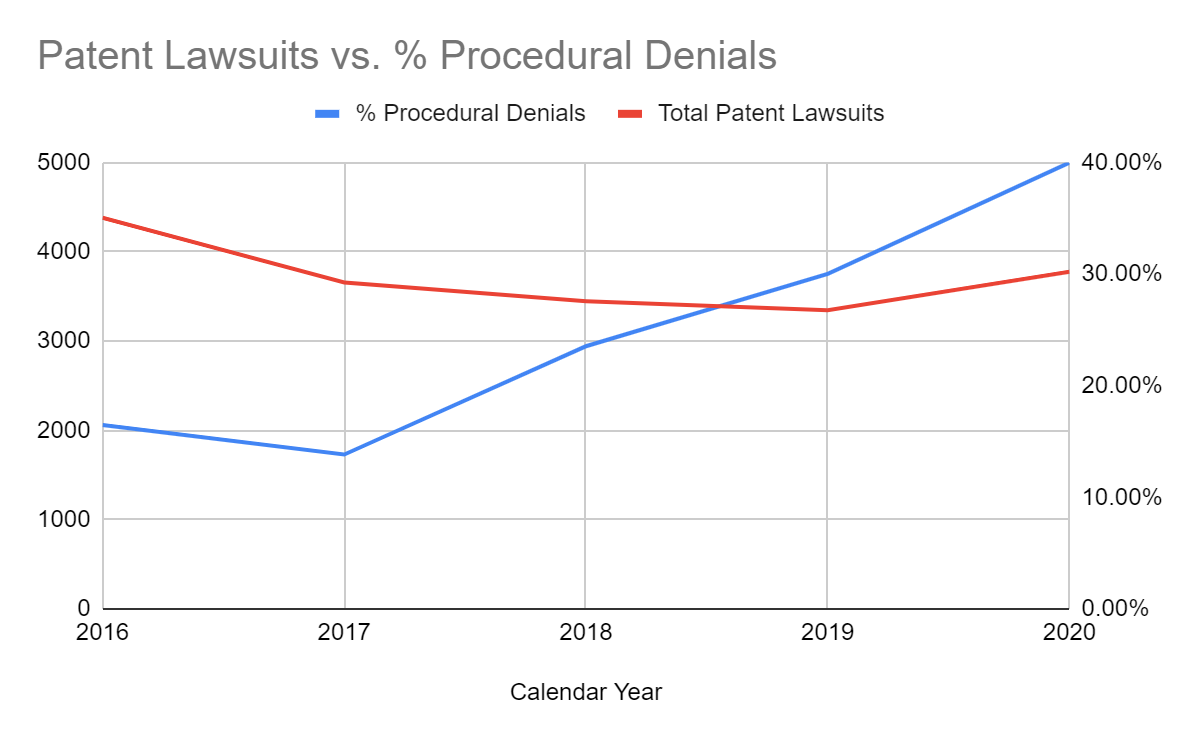
The following charts, created by Patent Progress, show the fallout from the discretionary denial precedents. The number of patent lawsuits, which had been falling, began to increase.
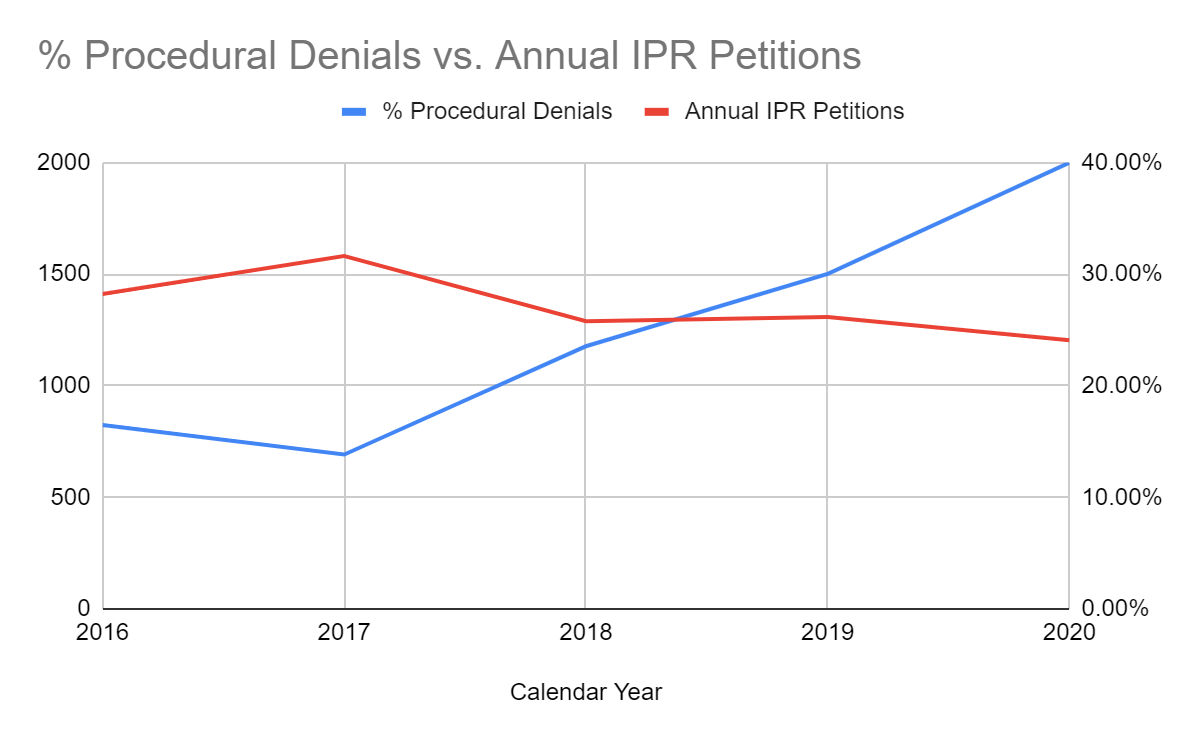
People started filing fewer IPRs.
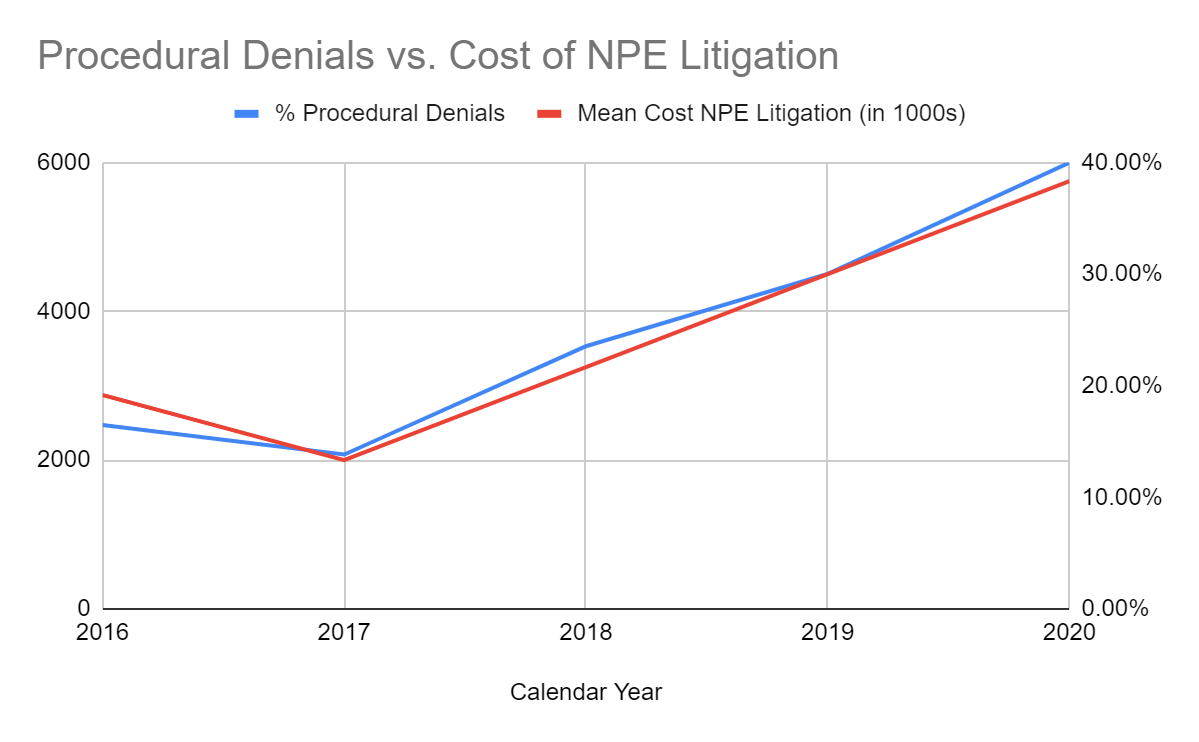
The cost of NPENon-Practicing Entity. A broad term associated with trolls but now disfavored because it includes universities and legitimate technology developers that seek to license technology in advance rather than after a producing company has independently developed it. More litigation increased in proportion to procedural denials.
The cost of IPRIntellectual Property Rights. Usually associated with formal legal rights such as patent, trademark, and copyright. Intellectual property is a broader term that encompasses knowledge, information, and data considered proprietary whether or not it is formally protected. increased as well. (While this graph shows the cost for electrical IPRs, other technologies experienced similar increases and IPRs on electrical technologies represent the majority of all IPRs.)
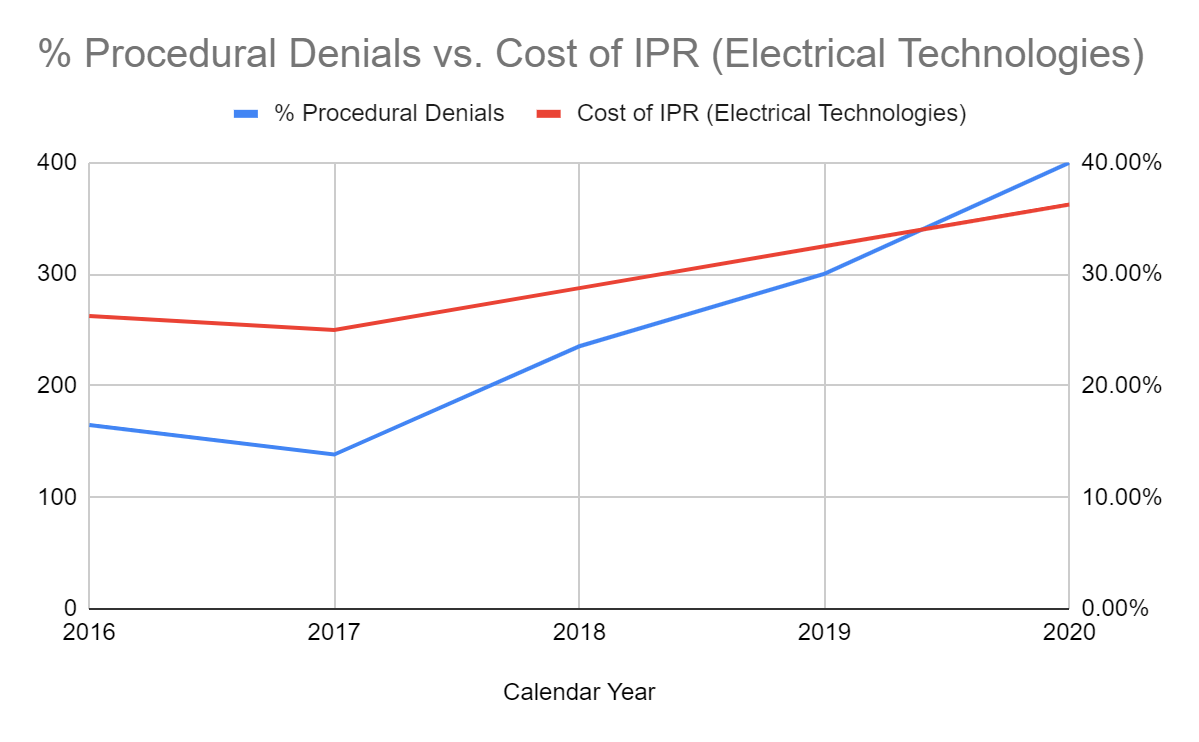
In other words, after the PTOPatent and Trademark Office, informally used interchangeably with USPTO. made the discretionary denial opinions precedential, innovators were more likely to face patent lawsuits, less likely to be able to use the IPRIntellectual Property Rights. Usually associated with formal legal rights such as patent, trademark, and copyright. Intellectual property is a broader term that encompasses knowledge, information, and data considered proprietary whether or not it is formally protected. process as a meaningful defense, and the total cost of defending themselves—both in court and at the PTAB—increased significantly.
It’s also increased the costs for patent owners, who face a more expensive set of proceedings at the Patent Office and more expensive litigation overall. While a discretionary denial might save them money at the Patent Office, it doesn’t provide a petitioner with any reason to back away from their invalidity theory—in fact, in cases like the recent Philip Morris IPRs, the petitioner might even be more likely to fight invalidity in court given the panel’s statement that their merits case was particularly strong. And without a reason to back away, petitioners are more likely to fight in court, increasing overall costs for patent owners.
Cui Bono?
So who actually wins here? Innovators—plaintiffs and defendants alike—are forced to spend more on less consistent proceedings, taking money away from their R&D efforts.The chief winners are patent lawyers and law firms, like Irell & Manella, Director Iancu’s former firm, which will have more trials to litigate, leading to more billable hours, and the patent trolls, like prolific filer Fortress Investment Group—represented by Irell & Manella in manycases—who receive higher value settlements when litigation costs increase.

